Key Takeaways:
- Ancient Treasure, Modern Concern: Chocolate’s rich history contrasts with today’s health concerns regarding heavy metal contamination.
- Choose Wisely, Indulge Safely: Selecting chocolates with lower heavy metals and advocating for transparency can mitigate health risks.
- Diversity in Delight: Varying chocolate types, including lower-risk milk and white chocolates, reduce exposure to cadmium and lead.
- Informed Choices, Healthier Lives: Awareness of cocoa origin and certified brands aids in safer consumption.
- Balance and Moderation: Enjoying chocolate in moderation, with a mindful approach, blends pleasure with health consciousness.
History and Origin
The history of cocoa cultivation dates back thousands of years to ancient civilizations such as the Olmec, Maya, and Aztec.
These cultures didn’t just snack on cocoa; they revered it. Cocoa beans were so valuable they were used as currency. Imagine buying a turkey with a handful of cocoa beans!
This rich history underscores cocoa’s long-standing value and versatility, well before it became the cornerstone of our favorite chocolate treats.
Types of Chocolate
When we talk about chocolate, we’re talking about a diverse family of sweets. There are four main types: white, milk, dark, and the relatively new ruby chocolate.
Their compositions vary significantly. For example, white chocolate, often debated if it should even be called chocolate, contains no cocoa solids—the source of both flavonols and heavy metals.
This absence places it in a unique position, health-wise, compared to its relatives.
Geographical Impact on Cadmium Levels
Not all chocolates are created equal, especially when it comes to heavy metals. Cacao beans from Latin America, especially Peru, are notorious for their high cadmium levels.
This contrasts with beans from West Africa, which tend to be much lower in these harmful elements. It’s a stark reminder that where your chocolate comes from can have a significant impact on its health implications.
Health Risks of Cadmium
Cadmium is no lightweight when it comes to health risks. This sneaky heavy metal in chocolate can accumulate in the body over time, leading to osteoporosis, kidney damage, and an increased risk of several cancers.
Cadmium’s deceit doesn’t end there; it mimics calcium, tricking the body into absorbing it. This Trojan horse act can have devastating long-term effects on health.
Introduction of Milk Chocolate
Henri Nestlé’s invention of milk chocolate was a game-changer. Adding sugar and milk transformed chocolate from a luxury good into a global blockbuster treat.
However, this sweet evolution wasn’t without its health implications. The added sugars and dairy bring their own set of concerns, complicating chocolate’s health narrative.
Selecting Safer Chocolates
There are ways to indulge more safely. Selecting chocolates with lower heavy metal levels and high flavanol content is key.
Some brands excel at this, offering products that maximize health benefits while minimizing risks. It’s about making informed choices in a sea of sweet temptation.
Cultural Evolution of Chocolate
The journey of chocolate from a bitter beverage to a beloved sweet treat is a story of transformation.
Facilitated by the Spanish conquest, chocolate’s spread across Europe marked its transition into the sugary confection we adore today. This cultural evolution reflects changing tastes and the inventive human spirit.
Contamination Process
Understanding how chocolate becomes contaminated with lead and cadmium is crucial. It begins with the growth of the cacao plant and continues through the processing stages of chocolate production.
Each step has potential contamination points, from soil to factory. It’s a complex chain that requires careful management to minimize health risks.
Health Benefits of Flavanols
Despite the concerns of heavy metals in chocolate, it’s not all doom and gloom. Dark chocolate, rich in flavanols, has been linked to health benefits.
Studies have shown that consuming high-flavonol cocoa products can improve walking performance in individuals with arterial diseases.
It’s a compelling argument for including high-quality dark chocolate in a balanced diet.
The line between the healthful indulgence of chocolate and risky business is thin. The journey from cocoa bean to chocolate bar is fraught with potential health hazards, yet also rich in historical and cultural significance.
Understanding the origins, types, and impacts of our choices becomes crucial. Whether you’re a fan of dark, milk, or white chocolate, informed decisions can help balance the scales between enjoyment and health.
Below are tables that show how heavy metal content can vary across chocolate varieties, emphasizing the importance of informed consumption choices.
Table 1: Cadmium Content in Different Types of Chocolate
| Type of Chocolate | Cadmium Content (micrograms per gram) |
| Dark Chocolate (>70% cocoa) | 0.8 – 1.5 |
| Milk Chocolate | 0.1 – 0.5 |
| White Chocolate | Negligible (No cocoa solids) |
| Ruby Chocolate | 0.5 – 0.9 |
Note: Dark chocolate contains the highest levels of cadmium due to its higher cocoa content. The European Union’s limit for cadmium in chocolate varies, allowing up to 0.8 micrograms per gram for chocolates containing 50%-70% cocoa solids, and 0.6 micrograms per gram for chocolates with less than 30% cocoa solids.
Table 2: Lead Content in Different Types of Chocolate
| Type of Chocolate | Lead Content (micrograms per gram) |
| Dark Chocolate (>70% cocoa) | 0.1 – 0.3 |
| Milk Chocolate | 0.05 – 0.1 |
| White Chocolate | Negligible (No cocoa solids) |
| Ruby Chocolate | 0.05 – 0.2 |
Note: The presence of lead in chocolate is generally lower than that of cadmium. However, even small amounts can pose health risks over time. The World Health Organization has set the acceptable daily intake for lead as no more than 3.6 micrograms per kilogram of body weight per week.
These tables highlight the variability in heavy metal content across different chocolate types, underscoring the need for consumers to be aware of what they are eating.
Dark chocolate, while rich in healthful flavanols, also carries higher amounts of cadmium and lead.
Conversely, white chocolate, lacking cocoa solids, shows negligible levels of these metals.
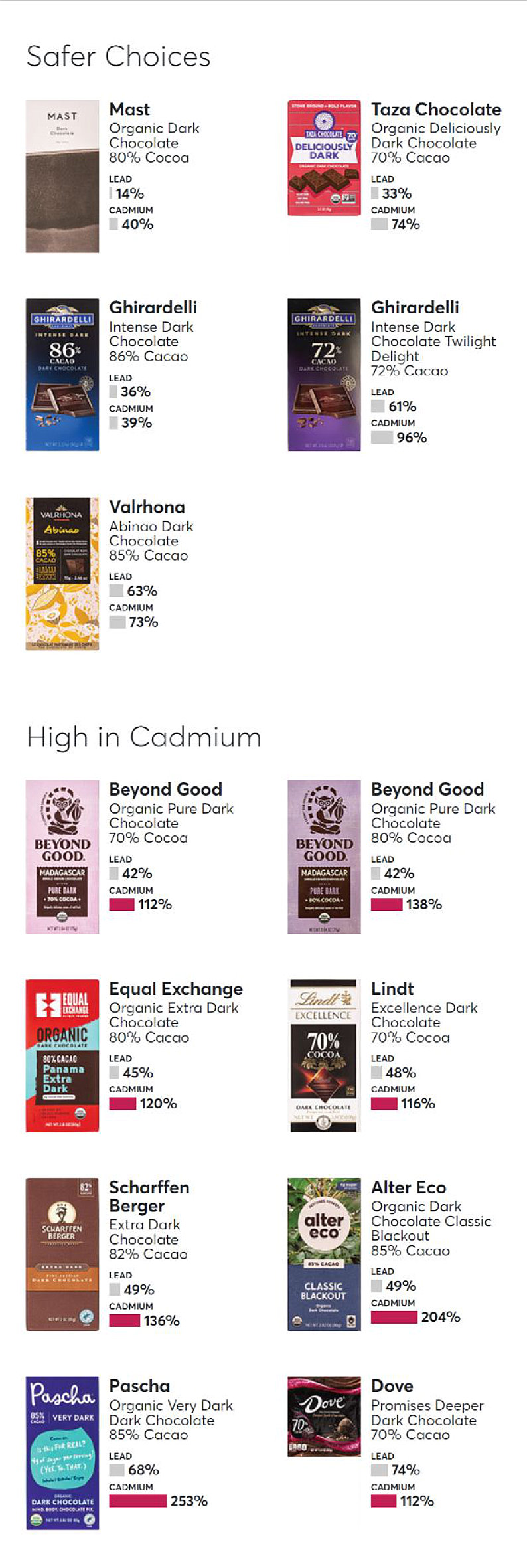
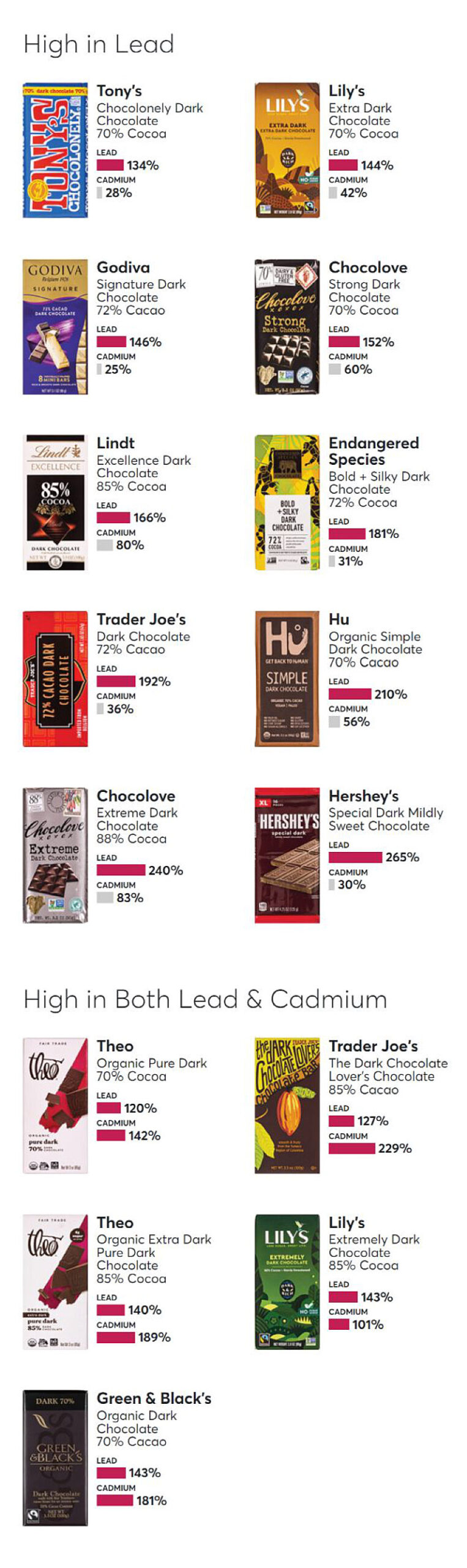
Brands That Have the Least to the Most Heavy Metals
Consumer Reports identified concerning levels of heavy metals in chocolate products from well-known brands including Hershey’s, Theo, and Trader Joe’s, among others.
Their report highlights which brands contained the highest amounts, as well as those that are considered safer options.
For 23 of the bars, eating just an ounce a day would put an adult over a level that public health authorities and CR’s experts say may be harmful for at least one of those heavy metals. Five of the bars were above those levels for both cadmium and lead. Consumer Reports
A Unique Profile of Potential Benefits and Risks
- Cocoa Origin and Heavy Metal Risk: The geographical origin of cocoa beans significantly influences the levels of heavy metals. Beans from Latin America may have higher cadmium levels, whereas those from West Africa are generally lower.
- EU Regulations on Heavy Metals: The European Union has strict regulations on the maximum levels of cadmium in chocolate products, demonstrating a proactive approach to consumer health. These regulations vary by the type of chocolate, with stricter limits for products consumed by children and those with higher cocoa content.
- Impact of Processing on Heavy Metal Content: The processing stages of chocolate production, including fermenting, drying, and roasting of cocoa beans, can affect the levels of heavy metals. However, contamination primarily occurs due to environmental factors such as soil and water.
- Choosing Low Heavy Metal Chocolates: Consumers can minimize their risk of heavy metal exposure by selecting chocolates from regions known for lower cadmium and lead levels, opting for brands that test for heavy metals, and varying their chocolate consumption across different types and brands.
- Health Benefits Versus Risks: While high-flavonol dark chocolate has been linked to health benefits such as improved cardiovascular health and cognitive function, the risk of heavy metal exposure, particularly from regular consumption of dark chocolate, poses a significant health concern that consumers need to weigh.
- Public Awareness and Labeling: There is a growing call for clearer labeling on chocolate products regarding their cocoa content, origin, and potential health risks, including heavy metal content, to better inform consumer choices.
Minimizing Exposure to Heavy Metals in Chocolate
- Opt for Certified Brands: Look for chocolates that have been certified by third-party organizations for lower heavy metal content. Certifications or direct statements regarding testing for heavy metals can be a good indicator of safer choices.
- Diversify Your Chocolate Consumption: Avoid consuming large quantities of dark chocolate regularly, as it typically has higher levels of heavy metals. Instead, vary your chocolate intake across different types, including milk and white chocolates, which generally contain lower levels of heavy metals.
- Consider the Origin of the Cocoa: Pay attention to where the cocoa in your chocolate comes from. Chocolates made from beans sourced from areas with lower soil contamination (like many regions in West Africa) are often lower in heavy metals.
- Moderation is Key: Enjoy chocolate as a treat rather than a diet staple. Consuming smaller amounts can reduce your overall exposure to cadmium and lead.
- Research Before You Buy: Some companies provide information about heavy metal testing on their websites or packaging. Doing some homework before making a purchase can help you choose safer products.
- Support Transparency in the Industry: Advocate for clear labeling regarding the cocoa content, origin, and any testing done for heavy metals. Supporting brands prioritizing transparency and consumer health can encourage broader industry shifts toward safer practices.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Being informed about the potential health risks and the factors that influence heavy metal content in chocolate can help you make healthier choices. Share what you learn with friends and family to spread awareness.
Final Thoughts About Heavy Metals in Chocolate
By adopting these practices, you can still enjoy chocolate while minimizing your risk of exposure to heavy metals in chocolate. It’s all about making smart, informed choices that balance your health with your enjoyment of this timeless treat.
As we stand in the aisles of confectionery making a choice of which to buy, we’re not just picking between milk or dark, but between ignorance and enlightenment.
The choice is ours. Do we pretend not to see, or do we face the bitter truth with the courage of cocoa warriors, ready to fight for our right to indulge wisely?
Let us not forget, during our quest for health, that chocolate was once divine—touted as a gift from the gods.
We have the power to demand better, to choose chocolates that are as clean as they are creamy, as pure as they are delicious.
So, fellow chocolate aficionados, let us embark on this journey with joy in our hearts and a bar of (responsibly sourced) chocolate in our hands.
In every bite, there’s a story of cultures, of love, of battles fought in the name of health and pleasure.
Chocolate is more than just a treat; it’s a testament to our ability to find balance, to enjoy the sweet without heavy metals in chocolate, and to live life with a taste for the extraordinary.
Here’s to making every chocolate choice a conscious one, savoring each piece with reverence for its journey, and never losing sight of the magic that a simple cocoa bean can bring into our lives.